People of different ages and socioeconomic backgrounds suffer from lower back pain and leg weakness, a prevalent illness. It frequently interferes with daily tasks and can range in intensity from a minor annoyance to incapacitating misery. The lower back or lumbar region, bears much of our body’s weight and is prone to various issues.
Leg weakness, when accompanied by lower back pain, can be a cause for concern. A person’s movement, balance and general quality of life can all be impacted by leg weakness. For diagnosis and treatment to be effective, it is essential to comprehend the relationship between lower back pain and leg weakness.
In basic terms, this article will go into the world of lower back pain and leg weakness. We’ll examine the reasons, signs and possible treatments, ensuring the information is clear. Whether you’re a person facing these difficulties or a caregiver who wants to learn more, this page has useful information.
Lower Back Pain Causes
Muscle Strains
Muscle strains are among the most common causes of lower back pain. These happen when the lower back muscles are strained or torn, frequently due to lifting large objects or making rapid movements.
Herniated Discs
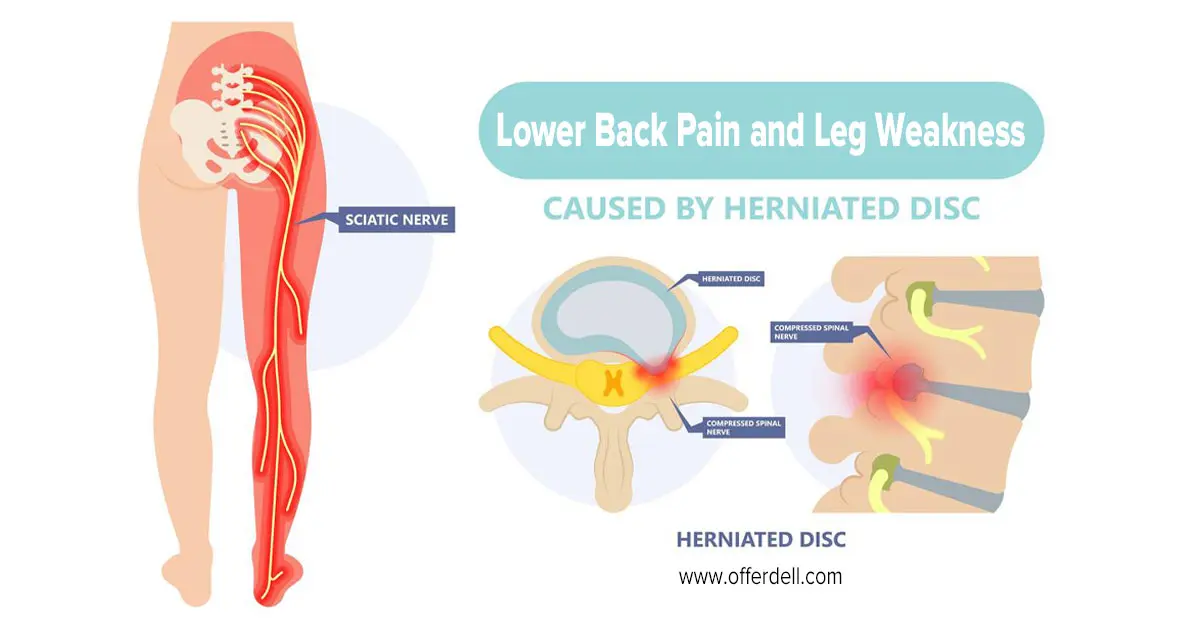
A herniated disc can press on nearby nerves, leading to lower back pain. Discs act as cushions between the spinal vertebrae; it can be painful when they bulge or rupture.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the spinal canal’s narrowing, which can pressure the spinal cord and nerves. This condition can cause lower back pain, especially in older people.
Sciatica
Sciatica is characterized by pain that radiates from the lower back down the leg. It occurs when the sciatic nerve is pinched or irritated, often due to a herniated disc.
Arthritis
Lower back joints can become painful and inflexible due to arthritis, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Trauma or Injury
Accidents, falls or injuries can damage the structures of the lower back, causing acute pain that may become chronic if not properly treated.
Relationship Between Back Pain and Leg Weakness
How Leg Weakness Develops
Lower back pain’s underlying causes frequently have a knock-on effect of leg weakness. The compression or irritation of lumbar nerves may cause leg weakness, numbness or tingling.
Nerve Compression
Herniated discs, spinal stenosis and other diseases can compress the nerves from the lower back to the legs. Weakness may result from this compression’s interference with the signals traveling from the brain to the legs.
Impact on Mobility
Leg weakness can significantly impact one’s ability to walk, climb stairs or stand for extended periods. This loss of mobility can have a deep impact on daily life and independence.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain often presents as a dull ache or sharp, stabbing pain in the lower back. It may be constant or intermittent and may worsen with certain movements.
Identifying Leg Weakness
Leg weakness is difficulty lifting the leg, walking or maintaining balance. A feeling of heaviness or instability may accompany it.
Medical Evaluation
If you’re experiencing persistent lower back pain and leg weakness, seeking medical evaluation is necessary. A healthcare provider can perform a complete physical examination to assess your condition.
Diagnostic Tests
To view the spine and determine the underlying causes of your problems, your doctor may prescribe diagnostic procedures like X-rays, MRIs or CT scans.
Treatment Options

Conservative Approaches
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help support the muscles in the lower back and improve flexibility, reducing pain and supporting the spine.
- Medication: Doctors may advise over-the-counter or prescription painkillers to treat pain and inflammation.
- Rest and Ice: Resting and applying ice to the affected area can relieve acute pain and reduce swelling.
Interventional Procedures
- Epidural Steroid Injections: Injections of anti-inflammatory medication into the epidural space can reduce pain and inflammation, especially when nerve compression is involved.
- Nerve Blocks: Nerve blocks target specific nerves causing pain and can provide temporary relief.
Surgical Solutions
- Microdiscectomy: To remove the herniated section of the disc and release pressure on the nerves, a microdiscectomy may be performed in cases of severe disc herniation.
- Spinal Fusion: Spinal fusion surgery stabilizes the spine by fusing two or more vertebrae. This procedure is considered for certain conditions, such as spinal instability.
Physical Therapy Exercises

Strengthening Exercises
Leg lifts and bridging are easy workouts that help build the lower back’s supporting muscles and ease the pain.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises can improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension. Gentle stretches like the knee-to-chest stretch can be beneficial.
Core Strengthening
A strong core is essential for spinal support. Exercises targeting the abdominal and back muscles can improve posture and reduce strain on the lower back.
Balance and Coordination
Balance exercises, such as standing on one leg or using a stability ball, can help improve coordination and prevent falls, especially if weakness is present.
Lifestyle Changes
Ergonomics
Improper posture at work or during daily activities can contribute to lower back pain. Adjusting ergonomics and maintaining good posture can make a significant difference.
Posture Correction
Conscious efforts to improve posture, such as sitting up straight and avoiding slouching, can help alleviate strain on the lower back.
Weight Management
Lower back pain can be made less severe by maintaining a healthy weight because doing so lessens the strain on the spine.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking has been linked to lower back pain, as it can impair blood flow to the spine. Quitting smoking can be a positive step toward pain management.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain Medications
Ibuprofen or acetaminophen, two over-the-counter painkillers, can offer momentary relief. Prescription medications may be considered for more severe pain.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Muscle spasms and pain can be reduced by applying heat or cold to the affected area. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation or TENS. Low-level electrical currents applied to the skin via TENS machines can block pain signals and offer comfort.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation)
TENS units deliver low-level electrical currents to the skin, disrupting pain signals and providing relief.
Coping with Chronic Pain
Psychological Impact
Mental health might suffer as a result of chronic pain. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of pain.
Support Groups
Joining support groups for individuals with chronic pain can provide a sense of community and valuable coping strategies.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation can help manage pain by promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
Surgery as a Last Resort
When Surgery is Considered
Surgery is typically considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief and the underlying condition is severe or progressive.
Surgical Risks
All surgical procedures carry some risk, including infection, bleeding and anesthesia complications. Discuss these risks with your surgeon before proceeding.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Recovery after surgery may require physical therapy and rehabilitation. Following post-operative instructions is crucial for a successful recovery.
Preventing Recurrence
Proper Body Mechanics
Learning and practicing proper body mechanics, especially during lifting or bending activities, can prevent future episodes of lower back pain.
Regular Exercise
The lower back can be kept healthy by following a regular workout regimen, combining strengthening and flexibility.
Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in nutrients can support overall health, including the health of your spine.
Alternative Therapies
Acupuncture
Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points of the body, which may help alleviate pain and promote relaxation.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments straighten the spine manually to minimize pain and enhance function.
Yoga and Tai Chi
These mind-body practices focus on flexibility, balance and relaxation, which can benefit individuals with lower back pain and leg weakness.
Complications and Red Flags
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Certain symptoms, such as loss of bowel or bladder control, severe weakness or sudden changes in sensation, require immediate medical attention.
Potential Complications
Untreated lower back pain and leg weakness can lead to chronic disability and reduced quality of life. Addressing these issues can prevent complications.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-life Experiences
Reading about others’ experiences with lower back pain and leg weakness can provide hope and insight into effective treatments.
Positive Outcomes
Many people have successfully managed and overcome lower back pain and leg weakness, leading fulfilling lives.
Summary
Key Takeaways
Lower back pain and leg weakness often go hand in hand due to various underlying causes. Early recognition, diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential for recovery.
Importance of Timely Intervention
Seeking help and following a structured treatment plan can prevent the progression of symptoms and improve one’s quality of life.
In conclusion, We summarize the key points throughout the article, highlighting the importance of understanding, early intervention and proper management.
We encourage readers to take their lower back pain and leg weakness seriously and to seek professional guidance when needed.
It’s important for you: How to Relieve Pain on Bottom of Foot: Simple Solutions